Self-assembly of supramolecular nanotubes/microtubes from 3,5-dimethyl-4-iodopyrazole for plasmonic nanoparticle organization†
Abstract
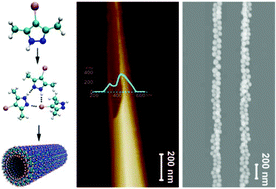
Hierarchical super-architectures from small molecule self-assembly have interesting properties and play an indispensable role in many fields. In most cases, a self-assembly process refers to multiple intermolecular interactions among intricately designed building blocks. Here, a supramolecular assembly with a tubular morphology with dimensions ranging from nanometers to micrometers was prepared through self-assembly of 3,5-dimethyl-4-iodopyrazole (DMIP), a molecule with an unprecedented simple structure. As predicted by density functional theory (DFT) calculations, the hydrogen bond and halogen bond interaction energy between DMIP molecules can be up to 32.81 kJ mol−1, which effectively drives DMIP molecules to assemble into fibrils, sheets, and finally, tubular architectures. Intriguingly, the formed tubular structure can be easily removed by heating at 100 °C, enabling the material to function as a disposable template to guide linear organization of nanostructures. As a proof of concept, ordered Au or Ag nanochains with diameters ranging from 18 to 120 nm were facilely prepared in high yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...