Biomimetic nanothylakoids for efficient imaging-guided photodynamic therapy for cancer†
Abstract
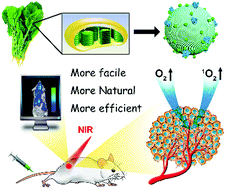
Biomimetic nanothylakoids, which are constructed from the thylakoid membrane of vegetable leaves, show high efficiency in tumor microenvironment modulation and photodynamic antitumor therapy under near infrared fluorescence guidance. Furthermore, their outstanding biosafety, facile preparation and low cost make nanothylakoids suitable for further clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...