Selective label-free detection of G-quadruplex structure of human telomere by emission spectral changes in visible-and-NIR region under physiological condition through the FRET of a two-component PPE-SO3−–Pt(ii) complex ensemble with Pt⋯Pt, electrostatic and π–π interactions†
Abstract
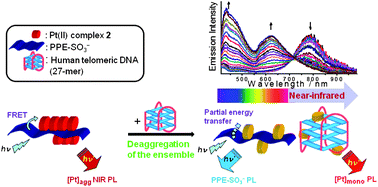
The formation of ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC6H5)](OTf)2 (2) is found to be the most efficient quencher of PPE-SO3− at both low and high concentrations. This has been ascribed to its low steric bulkiness and the stronger interactions with PPE-SO3−, and hence the largest association constant with PPE-SO3−, as well as the largest Förster radius, R0, among the complexes studied. The PPE-SO3−–2 ensemble has been employed in the detection of human telomere in aqueous
CC6H5)](OTf)2 (2) is found to be the most efficient quencher of PPE-SO3− at both low and high concentrations. This has been ascribed to its low steric bulkiness and the stronger interactions with PPE-SO3−, and hence the largest association constant with PPE-SO3−, as well as the largest Förster radius, R0, among the complexes studied. The PPE-SO3−–2 ensemble has been employed in the detection of human telomere in aqueous ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CC6H4CH2NMe3-4)](OTf)2 (1), which has a smaller association constant with PPE-SO3− and R0 value than 2. By modulation of the aggregation/deaggregation of the
CC6H4CH2NMe3-4)](OTf)2 (1), which has a smaller association constant with PPE-SO3− and R0 value than 2. By modulation of the aggregation/deaggregation of the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...