Enhanced bioactivity and bacteriostasis effect of TiO2 nanofilms with favorable biomimetic architectures on titanium surface
Abstract
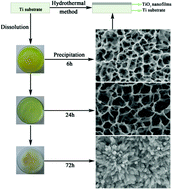
To improve the bioactivity and antibacterial properties of biomedical titanium implants, many efforts have been made to modify its surface composition and topography. In this work, biomimetic hierarchical micro/nanostructured titania films were formed on titanium surfaces via acid etching to generate microtopography and subsequent hydrothermal treatment to produce titania nanopetals or nanorod layers on it. In view of the potential clinical applications, the apatite-forming ability of the hierarchical micro/nano-textured TiO2 films was evaluated by simulated body fluid (SBF) immersion tests, and Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) were used to estimate the bacteriostatic effect. Meanwhile, the osteoblast-like cell line MG63 was cultured on the surface of the films to investigate their cytocompatibility. Compared to the microtopography, the hierarchical micro/nano-textured surfaces exhibit better apatite-forming ability and bacteriostatic effect on S. aureus, as well as enhancing the proliferation of MG63. The results obtained in this work suggest that the hierarchical micro/nano-textured TiO2 films on titanium may be a potential candidate for bone tissue engineering and biomedical implants. Our study reveals a synergistic effect on bioactivity and bacteriostasis as well as cell responses exerted by the titania nanofilms with biomimetic micro/nanotopographies and provides insight into the design of better biomedical implant surfaces.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Bioactive surfaces for hard tissue regeneration

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...