Preliminary anti-cancer photodynamic therapeutic in vitro studies with mixed-metal binuclear ruthenium(ii)–vanadium(iv) complexes†
Abstract
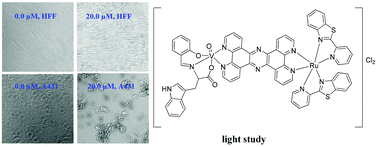
We report the synthesis and characterisation of mixed-metal binuclear ruthenium(II)–vanadium(IV) complexes, which were used as potential photodynamic therapeutic agents for melanoma cell growth inhibition. The novel complexes, [Ru(pbt)2(phen2DTT)](PF6)2·1.5H2O 1 (where phen2DTT =
- This article is part of the themed collection: Vanadium in Inorganic Chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...