Acid-functionalized UiO-66(Zr) MOFs and their evolution after intra-framework cross-linking: structural features and sorption properties†
Abstract
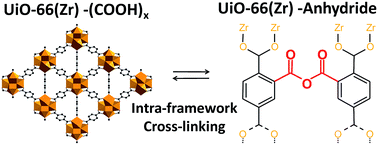
The functionalization of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) with free carboxylic groups is naturally difficult due to their potential coordination with metal ions. The impact of functionalizing the archetypical metal organic framework UiO-66(Zr) with free pending carboxylic groups was thus studied by a multi-technique approach. First, an environmentally friendly water synthesis route was developed to produce UiO-66(Zr)–(COOH)x (x = 1, 2) and the kinetics of crystallization was studied by in situ energy dispersive X-ray diffraction. In a second step, the structural features were studied by temperature-dependent X-ray diffractometry and further characterized by density functional theory calculations and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The gas sorption properties, acidity and conductivity features were respectively assessed by gas isotherms and calorimetry, infrared spectroscopy and complex impedance spectroscopy. These data show the noticeable influence of the introduced acidic groups. Finally, it was shown that the thermal treatment of such solids leads to an intra-framework cross-linking associated with the formation of anhydride bridges, as evidenced by FTIR and solid-state NMR, and modelled by DFT simulations. These species have a strong impact on the acidity, but a limited effect on gas sorption properties at room temperature. The reversibility of the carboxylic acids to anhydride transformation was also assessed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...