Phenolate platform for anion exchange in ionic liquids†
Abstract
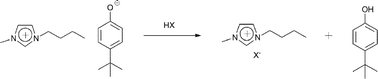
Water-soluble ionic liquids can be prepared from halide ionic liquids by a new anion exchange method. This new method for the anion exchange in ionic liquids takes advantage of the strong basicity of phenolate anions (also called phenate anions or phenoxide anions). The principle behind the method is to first prepare the 4-tert-butylphenolate salt of the desired cation, followed by reaction of the 4-tert-butylphenate with a Brønsted acid in a biphasic system formed by water and a water-immiscible organic solvent. The method has been applied to the synthesis of ionic liquids with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium, tetrabutylammonium, tetrabutylphosphonium and 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium cations and a range of anions (formate, acetate, methanesulfonate, tosylate, trifluoroacetate, picolinate, hydrogen dipicolinate, nicotinate, isonicotinate, nitrate, hydrogen sulfate, dihydrogen phosphate). Depending on the nature of the cation, slight modifications of the experimental procedure were required.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...