A novel multifunctional flame retardant MXene/nanosilica hybrid for poly(vinyl alcohol) with simultaneously improved mechanical properties†
Abstract
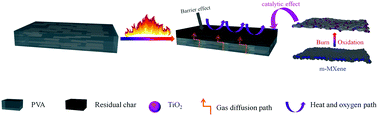
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is a biodegradable polymer with many ideal properties (such as excellent gas barrier properties, transparency and easy hydrolysis) and has a wide range of applications. However, its flammability is the main problem hindering its application in industry and life. Therefore, an effective flame retardant is needed to suppress its flammability while maintaining its own excellent performance. MXene, as a new graphene-like material has the prospect of being used in flame retardant polymers. However, the preparation of flame retardant MXene polymer nanocomposites has been hindered due to the MXene's poor interfacial compatibility with the polymer matrix. To solve this problem, nano-silica was deposited on the surface of MXene by hydrolyzing ethyl orthosilicate in situ and treating with a silane coupling agent. The effects of modified-MXene (m-MXene) on the PVA performance were studied by comparing the performances of PVA and m-MXene/PVA. The related results showed that m-MXene could significantly enhance the flame retardant performance, char formation capacity and the tensile properties of PVA. Specifically, the peak heat release rate (pHRR) of the m-MXene2/PVA nanocomposite with 2% m-MXene was 34.9% lower than that of pure PVA. The tensile strength and elongation at break of m-MXene2/PVA increased by 32.9% and 97% compared to those of pure PVA, respectively. The unique structure of m-MXene and its excellent dispersion, catalytic effect and barrier effect on PVA are the main reasons for improving these properties. This study provides a new strategy for the application of MXene in polymer nanocomposites, and enriches the application of MXene in the field of flame retardation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...