Uniform yolk–shell Sn4P3@C nanospheres as high-capacity and cycle-stable anode materials for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
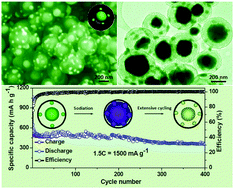
Uniform yolk–shell Sn4P3@C nanospheres were facilely synthesized via a top-down phosphorized route with yolk–shell Sn@C nanospheres as the precursor. As anode materials for Na-ion batteries, they exhibit very high reversible capacity (790 mA h g−1), superior rate capability (reversible capabilities of 720, 651, 581, 505, and 421 mA h g−1 at 0.2C, 0.4C, 0.8C, 1.5C, and 3C, respectively) and stable cycling performance (a high capacity of 360 mA h g−1 at 1.5C after long 400 cycles).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...