Very long Ag nanowire synthesis and its application in a highly transparent, conductive and flexible metal electrode touch panel†
Abstract
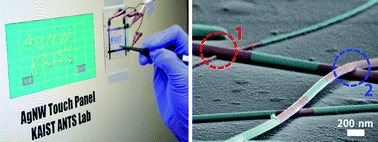
The future electronics will be soft, flexible and even stretchable to be more human friendly in the form of wearable computers. However, conventional electronic materials are usually brittle. Recently, carbon based materials are intensively investigated as a good candidate for flexible electronics but with limited mechanical and electrical performances. Metal is still the best material for electronics with great electrical properties but with poor transparency and mechanical performance. Here we present a simple approach to develop a synthesis method for very long metallic
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoscale 10th Anniversary: Top Cited Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...