Self-assembling modified neuropeptide S enhances nose-to-brain penetration and exerts a prolonged anxiolytic-like effect†
Abstract
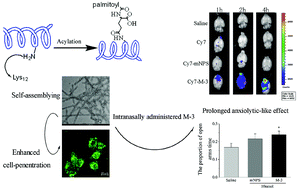
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental diseases and can greatly disrupt everyday life. Although there has been substantial research on anxiety disorders, novel therapeutics are needed. Neuropeptide S (NPS) is a potential therapeutic candidate owing to its strong anxiolytic activity; however, some disadvantages, such as its poor metabolic stability and inability to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), limit its use in the clinic. Herein, inspired by nose-to-brain drug delivery strategies, an endogenous 20-amino-acid-long mNPS peptide was modified by incorporating palmitic acid into its functional Lys12 side chain (M-3), which was expected to facilitate nose-to-brain penetration and exert a prolonged anxiolytic-like effect compared to mNPS. We found that M-3 assembled into nanofibers that retained the bioactivity of NPS and exhibited obvious improvements in metabolic stability. Notably, as expected, self-assembled M-3 was able to penetrate into the brain and exert anxiolytic effects. The elevated plus-maze (EPM) results further revealed that M-3 could produce prolonged anxiolytic-like effects in mice. In vivo imaging studies revealed that self-assembled M-3 could be efficiently transported from the nasal cavity to the brain. Furthermore, when intranasally administered, this molecule exhibited a significantly prolonged anxiolytic-like effect, which further illustrated that this molecule has a potent nose-to-brain penetration in vivo. Overall, this self-assembled nanofiber showed potent nose-to-brain penetration ability and prolonged bioactivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...