A mechanistic investigation of carbon–hydrogen bond stannylation: synthesis and characterization of nickel catalysts†
Abstract
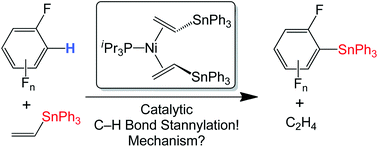
The complex (iPr3P)Ni(η2-Bu3SnCH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)2 (1a) was characterized by
CH2)2 (1a) was characterized by ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, which generates C6F5SnBu3 and
CH2, which generates C6F5SnBu3 and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2)2 (1b) provides a more easily handled analogue, and is also capable of catalytic
CH2)2 (1b) provides a more easily handled analogue, and is also capable of catalytic ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 and C6F5H. Mechanistic studies on 1b show that the catalytically active species remains mononuclear. The rate of catalytic
CH2 and C6F5H. Mechanistic studies on 1b show that the catalytically active species remains mononuclear. The rate of catalytic ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2]. This is consistent with a mechanism where reversible Ph3SnCH
CH2]. This is consistent with a mechanism where reversible Ph3SnCH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 dissociation provides (iPr3P)Ni(η2-Ph3SnCH
CH2 dissociation provides (iPr3P)Ni(η2-Ph3SnCH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), followed by a rate-determining reaction with C6F5H to generate the stannylation products. Kinetic competition reactions between the fluorinated aromatics
CH2), followed by a rate-determining reaction with C6F5H to generate the stannylation products. Kinetic competition reactions between the fluorinated aromatics
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent: Americas

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...