Efficient conversion of spent mushroom substrate into a high value-added anticancer drug pentostatin with engineered Cordyceps militaris†
Abstract
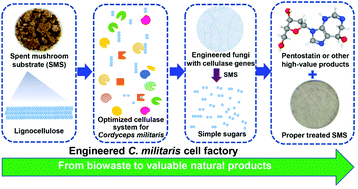
Spent mushroom substrate (SMS) is lignocellulosic waste that contributes to environmental pollution. The entomogenous fungus Cordyceps militaris cannot utilize the cellulose in SMS for growth, but it can produce a series of bioactive compounds, including the FDA-approved first-line anticancer drug pentostatin. To efficiently utilize SMS, we engineered C. militaris to convert SMS into pentostatin. We optimized the composition ratio of a cellulase combination to obtain the best performance on SMS in vitro. The introduction of the optimized cellulase system in C. militaris led to strong hydrolytic activity towards cellulose, and the filter paper activity of one engineered strain, CmTX, reached 0.82 ± 0.02 U mL−1. The titer of pentostatin in CmTX under submerged fermentation with SMS as the substrate was 434.3 mg L−1, which was 2.32-fold that of the wild-type strain fermented in Sabouraud dextrose broth. CmTX under solid-state fermentation with SMS yielded 1.45 mg of pentostatin per gram of dried SMS. The production was further increased by 39.2% via a biasing metabolic flux from the cordycepin synthesis to pentostatin pathway. Although other strategies can produce pentostatin from glucose and other easily fermentable hexoses, the yield and titer of pentostatin in our engineered C. militaris strain with SMS as the substrate were 10-fold of those in previous reports. Compared with the chemical synthesis of pentostatin, our biological strategy overcomes the stereoselectivity of the chiral alcohol structure and glycoside groups during pentostatin synthesis. We successfully demonstrated that engineered C. militaris can produce valuable products using SMS as a substrate instead of a range of catalysts and complex chemicals, which enables green and sustainable SMS pollution removal while biosynthesizing a high-value anticancer drug.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...