An aminoglycoside antibiotic inhibits both lipid-induced and solution-phase fibrillation of α-synuclein in vitro†
Abstract
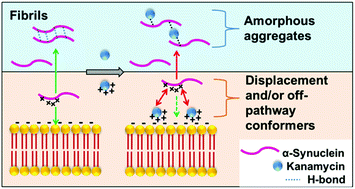
Parkinson's disease (PD), closely associated with the misfolding and aggregation of the neuronal protein α-synuclein (A-Syn), is a neurodegenerative disorder with no cure to date. Here, we show that the commercially available, inexpensive, aminoglycoside antibiotic kanamycin effectively inhibits both lipid-induced and solution-phase aggregation of A-Syn in vitro, pointing towards the prospective repurposing of kanamycin as a potential anti-PD drug.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...