Ergothioneine exhibits longevity-extension effect in Drosophila melanogaster via regulation of cholinergic neurotransmission, tyrosine metabolism, and fatty acid oxidation†
Abstract
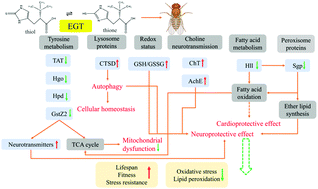
Many studies have demonstrated the protective effect of ergothioneine (EGT), the unique sulfur-containing antioxidant found in mushrooms, on several aging-related diseases. Nevertheless, to date, no single study has explored the potential role of EGT in the lifespan of animal models. We show here that EGT consistently extends fly lifespan in diverse genetic backgrounds and both sexes, as well as in a dose and gender-dependent manner. Additionally, EGT is shown to increases the climbing activity of flies, enhance acetylcholinesterase (AchE) activity, and maintain the ratio of reduced glutathione (GSH) to oxidized glutathione (GSSG)of aged flies. The increase in lifespan by EGT is gut microorganism dependent. We proposed potential mechanisms of lifespan extension in Drosophila by EGT through RNA-seq analysis: preservation of the normal status of the central nervous system via the coordination of cholinergic neurotransmission, tyrosine metabolism, and peroxisomal proteins, regulation of autophagic activity by altering the lysosomal protein CTSD, and the preservation of normal mitochondrial function through controlled substrate feeding into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, the major energy-yielding metabolic process in cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...