Local structure relaxation, quantum trap depression, and valence charge polarization induced by the shorter-and-stronger bonds between under-coordinated atoms in gold nanostructures
Abstract
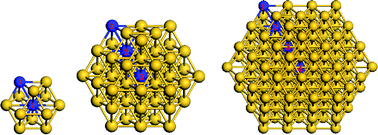
Relativistic density functional theory calculations have been conducted to examine the effect of atomic under-coordination on the crystal structure, binding energy, and electron configuration of cuboctahedral and Marks decahedral gold clusters. Trend consistency between calculations and experimental observations confirmed the predictions made using BOLS correlation theory, suggesting that the shorter-and-stronger bonds between under-coordinated atoms induce local structure relaxation, potential well depression, and the associated local charge and energy densification, as well as the polarization of the otherwise conducting s-electrons (valence charge) by the densely- and tightly-trapped core electrons of which the binding energy shifts positively to deeper energies. Findings are in good agreement with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...