Pediococcus pentosaceus PP04 improves high-fat diet-induced liver injury by the modulation of gut inflammation and intestinal microbiota in C57BL/6N mice†
Abstract
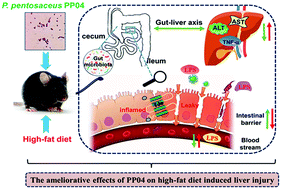
In this study, Pediococcus pentococcus PP04 (PP04) isolated from the Northeast pickled cabbage was given to C57BL/6N mice for eight weeks, aiming to investigate the ameliorative effects of PP04 on liver injury induced by a high-fat diet. The western blot results suggested that PP04 ameliorated the increase of intestinal permeability by dramatically increasing the expressions of tight junction proteins, such as Occludin, Claudin-1 and ZO-1, which decreased hepatic lipopolysaccharides (LPS), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) concentrations to effectively alleviate the liver injury. Furthermore, PP04 relieved the high-fat diet-caused gut inflammation by the NF-κB/Nrf2 signaling pathway, which regulated the expression of inflammatory cytokines and antioxidants, to positively improve the liver injury. In addition, the 16S rDNA sequencing results inferred that PP04 had the potential to rebalance intestinal flora disorders through regulating the relative abundance of inflammation and obesity-related bacteria in mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...