Photocatalytic decarboxylation of lactic acid by Pt/TiO2†
Abstract
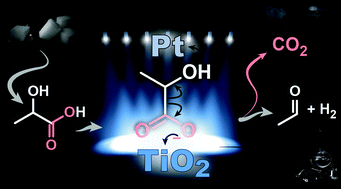
A photocatalytic route for the conversion of lactic acid to acetaldehyde in water is demonstrated. Direct UV photolysis of lactic acid yields CO2 and ethanol via a radical mechanism. Pt/TiO2 considerably increases the rate of lactic acid decarboxylation with acetaldehyde, H2 and CO2 as the main products. A concerted photodecarboxylation/dehydrogenation mechanism is proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...