Surfactant assisted reactive crystallization of cobalt oxide nanoparticles in a tubular microreactor: effects of precursor concentrations and type of surfactants
Abstract
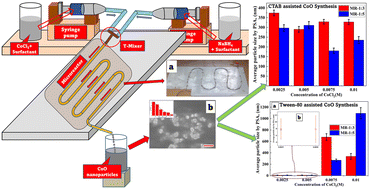
Cobalt oxide (CoO) nanoparticles were synthesized via a surfactant assisted reactive crystallization route using cobalt chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4) in an indigenous lab-scale tubular microreactor. The effects of the precursors' concentrations, flow rate and type of surfactants on particle size distribution, average particle size (dAvg) and aggregation of synthesized CoO nanoparticles were investigated. The initial molar ratios of the precursors' concentrations (CoCl2·6H2O : NaBH4) were kept as 1 : 3 and 1 : 5 by varying the CoCl2·6H2O concentrations in the range of 0.0025–0.01 M. CTAB and Tween 80 were used as surfactants. Results revealed that Tween 80 as a superior surfactant to CTAB for both the molar ratios, in combination with dilute precursors (0.0025 M CoCl2·6H2O) and minimum flow rates, yields CoO nanoparticles with dAvg < 10 nm with narrow size distributions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...