Synthesis of porous Cu2O/CuO cages using Cu-based metal–organic frameworks as templates and their gas-sensing properties†
Abstract
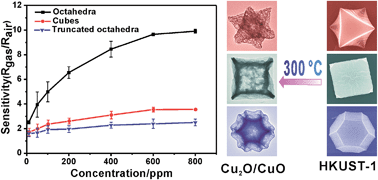
Shape-controllable porous, hollow metal oxide cages are attracting more and more attention due to their widespread applications. In this paper, octahedral, truncated octahedral and cubic Cu2O/CuO cages were successfully fabricated by the thermal decomposition of the polyhedral crystals of Cu-based metal–organic frameworks (Cu-MOFs) as self-sacrificial templates at 300 °C. The morphology of the Cu-MOF polyhedral precursors was well tuned by using lauric acid as the growth modulator under solvothermal conditions. Gas-sensing measurements revealed that the octahedral Cu2O/CuO cages exhibited a gas-sensing performance far better than those exhibited by truncated octahedral and cubic cages, which is attributed to the cooperative effect of the large specific surface area (150.3 m2 g−1) and high capacity of surface-adsorbed oxygen of the octahedral Cu2O/CuO cages.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...