A first principles study of oxygen reduction reaction on a Pt(111) surface modified by a subsurface transition metal M (M = Ni, Co, or Fe)†
Abstract
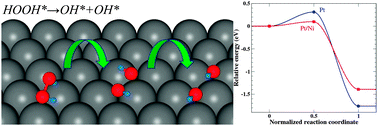
We have performed first-principle density functional theory calculations to investigate how a subsurface transition metal M (M = Ni, Co, or Fe) affects the energetics and mechanisms of oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) on the outermost Pt mono-surface layer of Pt/M(111) surfaces. In this work, we found that the subsurface Ni, Co, and Fe could down-shift the d-band center of the Pt surface layer and thus weaken the binding of chemical species to the Pt/M(111) surface. Moreover, the subsurface Ni, Co, and Fe could modify the heat of reaction and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...