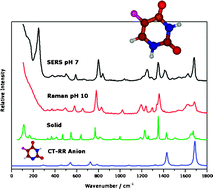
Raman and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) have been recorded under several experimental conditions. SERS spectra have been analysed according to a resonant charge-transfer (CT) mechanism similar to a resonance Raman (RR) process, involving the photoinduced transfer of an electron from the Fermi level of the metal to vacant orbitals of the adsorbate (SERS-CT). In order to detect the enhancement mechanism and to identify the chemical species that give rise to the spectra, the theoretical SERS-CT intensities for the dienolic and diketo forms, and its respective N1 and N3 deprotonated anions (5-FU−), have been calculated and compared with the experimental results. In this way, the presence of N1 deprotonated anion is confirmed by SERS given that the calculated SERS-CT intensities predict the selective enhancement of the band at ca. 1680 cm−1 in agreement with the experiment. Therefore, the metal-to-adsorbate CT process involves the transient formation of the respective radical dianion (5-FU˙2−), which is new evidence of the relevance of the CT enhancement mechanism in SERS.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...