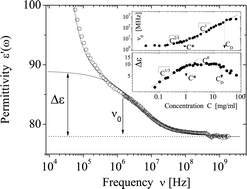
The dielectric relaxations associated with counterion polarization along some typical polyion lengths have been measured in an extended frequency range (from 10 kHz to 2 GHz) for four different polyelectrolyte solutions, differing for the polyion molecular weight and the backbone stiffness. Here, we deal with the so-called intermediate dielectric relaxation, falling between the polarization process concerning the whole polyion chain and the polarization process associated with the field-induced re-orientation of the water molecule dipoles. These observed intermediate relaxations have been characterized by means of two parameters, i.e., the dielectric strength Δε and the relaxation frequency ν0, and their dependence on the polyion concentration has been described according to the scaling model of a polyelectrolyte solution. These dependencies follow the expected exponents of the scaling laws, both for the dilute and semidilute (unentangled and entangled) regimes. The different concentration regimes evidenced from dielectric relaxation measurements are in very good agreement with the ones determined by means of the zero-shear viscosity measurements. Our results confirm that the intermediate dielectric relaxation in polyelectrolyte solutions should be attributed to counterion fluctuations along some segments (e.g. the subunits of the Mandel model) of the polyion chain, independently of its overall stiffness. This counterion polarization effect is rather confined to the local structure of the polyion chain instead of the whole chain and it is largely independent of the polyion conformation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...