Study of dispersion mechanisms of modified SiC powder: electrostatic repulsion and steric hindrance mechanism†
Abstract
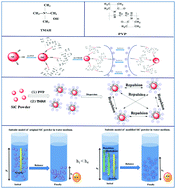
Surface modification technology was used to increase the dispersion of SiC powder. A slurry with high stability was fabricated using modified SiC powder with high dispersibility. The relative settlement height (RSH) of the slurry was maintained at 72.5% after 30 hours, indicating the high stability of SiC powder co-modified with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide (TMAH) in water medium. Meanwhile, the minimum viscosity of 0.322 Pa s was obtained at 45 vol% solid content, and the maximum solid content of the slurry was 64.6 vol%. In addition, the maximum zeta potential of modified SiC powder was −58.5 mV, indicating strong electrostatic repulsion among particles. Therefore, the modified SiC powder shows high dispersion. More important is that the effect of the dispersion mechanism on the performance of modified SiC powder was investigated in depth. TMAH, as one of the excellent dispersants, can increase the electrostatic repulsion among particles significantly, facilitating the preparation of the slurry with low viscosity and high solid content. However, PVP, as one of the neutral polymers with hydrophilicity, plays an important role in maintaining the stability of the slurry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...