Folic acid-modified Prussian blue/polydopamine nanoparticles as an MRI agent for use in targeted chemo/photothermal therapy†
Abstract
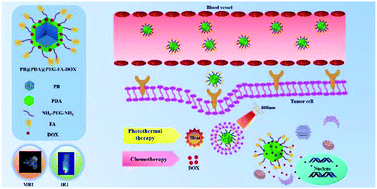
Fabricating multifunctional theranostic nanoparticles is highly pursued but still challenging for effective cancer treatment. Herein is reported a new theranostic nanoagent as both an MRI and targeted chemo/photothermal therapeutic agent. Prussian blue nanoparticles (PB) were first decorated with polydopamine (PDA), then conjugated with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and folic acid (FA), and finally loaded with doxorubicin (DOX) (denoted as PB@PDA@PEG-FA-DOX). The nanoagent was estimated to have an average size of 40 nm with a DOX-loading capacity of 36%, photothermal conversion efficiency of 45.7% and a transverse relaxation rate of 0.366 mM−1 s−1. In vitro release investigations showed a dual-responsive release by a mild acid and near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation. PB@PDA@PEG-FA illustrated negligible cytotoxicity against the HL-7702 cell line and 38.2% cell viability under NIR against the HeLa cell line. PB@PDA@PEG-FA-DOX exhibited 45.2% cell viability. In contrast, the cell viability of PB@PDA@PEG-FA-DOX was dramatically decreased to 18.4% under NIR. Exclusive of folic acid, PB@PDA@PEG-DOX demonstrated 40.5% cell viability. These results demonstrated the potential of the nanoagent for integrated photothermal therapy (PTT) and chemotherapy, also embracing the FA targeting effect. In vivo MRI confirmed the effective nanoparticle accumulation, while infrared thermal images revealed the dramatically increased temperature under NIR at a tumor site. In vivo combination treatment-induced tumors were nearly completely destroyed without significant body weight loss after 14 days. H&E and Ki67 staining indicated remarkable necrosis and weak cell proliferation in the tumor area. Histologic examination revealed a lower toxicity in the vital organs. Therefore, this combination of chemo/photothermal therapy could provide an efficient route for cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...