Palladium(0)-catalyzed direct cross-coupling reaction of allylic alcohols with aryl- and alkenylboronic acids†
Abstract
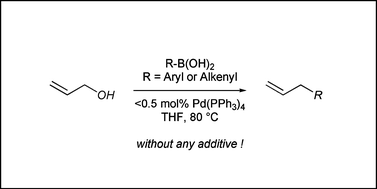
Allylic alcohols can be used directly for the palladium(0)-catalyzed allylation of aryl- and alkenylboronic acids with a wide variety of functional groups. A triphenylphosphine-ligated palladium catalyst turns out to be most effective for the cross-coupling reaction and its low loading (less than 1 mol%) leads to formation of the coupling product in high yield. The Lewis acidity of the organoboron reagents and poor leaving ability (high basicity) of the hydroxyl group are essential for the cross-coupling reaction. The reaction process is atom-economical and environmentally benign, because it needs neither preparation of allyl halides and esters nor addition of stoichiometric amounts of a base. Furthermore, allylic alcohols containing another unsaturated carbon–carbon bond undergo arylative cyclization reactions leading to cyclopentane formation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemistry Nobel 2010 Web Collection: Cross-coupling reactions in organic chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...