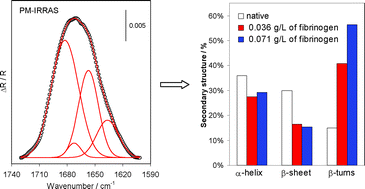
Adsorption of fibrinogen on a biomedical-grade stainless steel 316LVM surface: a PM-IRRAS study of the adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and secondary structure changes
Abstract
Polarization-modulation infrared reflection–absorption
- This article is part of the themed collection: Highlighting Canadian research in PCCP

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...