Comprehensive analysis of the lncRNA-associated ceRNA network identifies neuroinflammation biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease†
Abstract
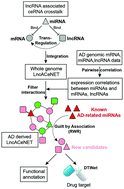
Accumulating evidence has highlighted the important roles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) acting as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) in Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we constructed an AD-derived lncRNA-associated ceRNA network (LncACeNET) based on the ceRNA hypothesis and co-expressed correlation analysis of RNAs (miRNAs, mRNAs and lncRNAs) from AD patients. Based on this network, we preliminarily identified new potential AD biomarkers including hsa-miR-155-5p, CERS6-AS1, and CTB-89H12.4. The functional enrichment analysis demonstrated that these inferred biomarkers were significantly correlated with AD-related biological processes such as neuron projection development and neuron projection morphogenesis. Notably, lncRNA CTB-89H12.4 is significantly associated with “calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter”, “chemical synaptic transmission”, “presynaptic membrane assembly”, “receptor localization to synapse”, and “learning”. This indicates the important role of CTB-89H12.4 as a promising target for AD therapy. Subsequently, we used the computational pipeline DTINet and discovered 19 lines of probable therapeutic relationships between FDA-approved drugs and CTB-89H12.4, which offered a new avenue to repurpose existing FDA-approved drugs for AD indication. Our study provides a new landscape for LncACeNET in AD, and will benefit mechanism study and new drug development for AD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...