Green synthesis of porous β-cyclodextrin polymers for rapid and efficient removal of organic pollutants and heavy metal ions from water†
Abstract
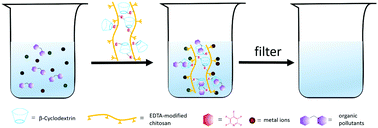
Metal ions and organic pollutants pose a serious threat to public health and are often found to coexist in industrial wastewaters. Herein, we developed a general route for the synthesis of porous polymers by joining β-cyclodextrin (β-CD), EDTA-modified chitosan (CS-EDTA) (the chitosan could be substituted by other biomass polymers) and pentafluoropyridine together, and using biomass-derived 2-methyltetrahydrofuran as an environmentally benign solvent. Some of these as-prepared porous polymers could be used as very attractive and effective adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants and heavy metal ions such as Pb(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Co(II), Hg(II), and Cr(II) from wastewater simultaneously with very fast uptake kinetics compared to other adsorbents. The as-prepared porous polymers from β-CD and CS-EDTA, cellulose, sodium alginate, or alkali lignin were named P-CDEC, P-CDMCC, P-CDSA, and P-CDAL, respectively. Taking P-CDEC as an example, k2 (18.6 g mg−1 min−1 for Pb(II) and 4.9 g mg−1 min−1 for trichlorophenol) is one to three orders of magnitude higher than that of other common adsorbents. More importantly, the polymers can be recycled and after five cycles, more than 91% adsorption capacity still remained. Therefore, these polymers are potential materials for integrative and efficient treatment of coexisting toxic pollutants. The as-developed green route for the synthesis of porous polymers from biomass could be extended for the preparation of other functional materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...