Bacillus subtilis biofilms characterized as hydrogels. Insights on water uptake and water binding in biofilms†
Abstract
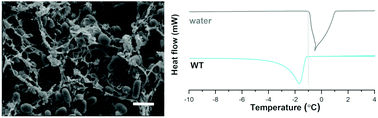
Biofilms are aggregates of cells that form on surfaces or at the air–water interface. Cells in a biofilm are encased in a self-secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) that provides them with mechanical stability and protects them from antibiotic treatment. From a soft matter perspective, biofilms are regarded as colloidal hydrogels, with the cells playing the role of colloids and the ECM compared with a cross-linked hydrogel. Here, we examined whole biofilms of the soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis utilizing methods that are commonly used to characterize hydrogels in order to evaluate the uptake of water and the water properties in the biofilms. Specifically, we studied wild-type as well ECM mutants, lacking the protein TasA and the exopolysaccharide (EPS). We characterized the morphology and mesh size of biofilms using electron microscopy, studied the state of water in the biofilms using differential scanning calorimetry, and finally, we tested the biofilms' swelling properties. Our study revealed that Bacillus subtilis biofilms resemble cross-linked hydrogels in their morphology and swelling properties. Strikingly, we discovered that all the water in biofilms was bound water and there was no free water in the biofilms. Water binding was mostly related with the presence of solutes and much less so with the major ECM components, the protein TasA and the polysaccharide EPS. This study sheds light on water uptake and water binding in biofilms and it is therefore important for the understanding of solute transport and enzymatic function inside biofilms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...