Improved stability and activity of Fe-based catalysts through strong metal support interactions due to extrinsic oxygen vacancies in Ce0.8Sm0.2O2−δ for the efficient synthesis of ammonia†
Abstract
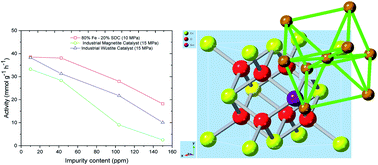
In this article, hematite α-Fe2O3 was used as the precursor for the iron-based ammonia synthesis catalyst. Ce0.8Sm0.2O2−δ (SDC), with extrinsic oxygen vacancies was used as a promoter for forming an Fe–SDC composite catalyst. The new Fe–SDC catalyst achieves both high catalytic activity and excellent oxygenate tolerance, working with excellent stability at a feed-gas purity of 99.996%. At 500 °C, 10 MPa for the 80% Fe–20% SDC catalyst, and 15 MPa for the industrial Fe catalysts, and at an impurity level of 150 ppm, with known injected 107.5 ppm O2, the activity of Fe–SDC retains 47.3% of that measured in purified gases while it is only 26.4% and 7.6% for the wüstite and magnetite – based industrial Fe catalysts respectively. It is believed that the introduction of extra extrinsic oxygen vacancies strengthen the strong metal-support interaction (SMSI), preventing the growth of formed Fe particles, leading to excellent stability and high tolerance to oxygenates. The SMSI between Fe and oxygen vacancies in SDC may also help to weaken and break the strong N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N bonds in N2, increasing the catalytic activity. The use of promoters with extrinsic oxygen and potentially other anion vacancies provides a new strategy to develop oxygenate tolerant catalysts for efficient synthesis of ammonia from less pure feed gases at reduced pressures.
N bonds in N2, increasing the catalytic activity. The use of promoters with extrinsic oxygen and potentially other anion vacancies provides a new strategy to develop oxygenate tolerant catalysts for efficient synthesis of ammonia from less pure feed gases at reduced pressures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...