Luminescent hybrid halides with various centering metal cations (Zn, Cd and Pb) and diverse structures†
Abstract
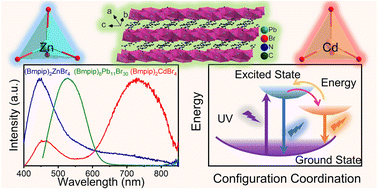
Organic–inorganic hybrid metal halides have been extensively studied because of their great potential in optoelectronics. Herein, we report three hybrid metal halides (Bmpip)2ZnBr4, (Bmpip)2CdBr4, and (Bmpip)8Pb11Br30 (where Bmpip+ is 1-butyl-1-methyl-piperidinium, C10H22N+). (Bmpip)2ZnBr4 and (Bmpip)2CdBr4 crystallize in the P21/c space group with zero-dimensional crystal structures with [MBr4]2− (M = Zn, Cd) tetrahedra isolated by Bmpip+. (Bmpip)8Pb11Br30 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) with one-dimensional corrugated chains constructed from face-sharing [PbBr6]4− octahedra. All of the compounds exhibit excellent ambient and thermal stability. Under UV excitation, all three compounds exhibit very broad emissions. Temperature-dependent photoluminescence measurements indicate that the broad emissions of (Bmpip)2ZnBr4 and (Bmpip)2CdBr4 can be attributed to both the organic cations and self-trapped excitons (STEs) and that the emission of (Bmpip)8Pb11Br30 is assigned to STEs. Density functional theory calculations reveal that the three compounds adopt a direct band gap. This work enriches our understanding of the structure types of hybrid metal halides while revealing their diverse emission mechanisms.
with one-dimensional corrugated chains constructed from face-sharing [PbBr6]4− octahedra. All of the compounds exhibit excellent ambient and thermal stability. Under UV excitation, all three compounds exhibit very broad emissions. Temperature-dependent photoluminescence measurements indicate that the broad emissions of (Bmpip)2ZnBr4 and (Bmpip)2CdBr4 can be attributed to both the organic cations and self-trapped excitons (STEs) and that the emission of (Bmpip)8Pb11Br30 is assigned to STEs. Density functional theory calculations reveal that the three compounds adopt a direct band gap. This work enriches our understanding of the structure types of hybrid metal halides while revealing their diverse emission mechanisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...