A molecular dynamics study of bond exchange reactions in covalent adaptable networks†
Abstract
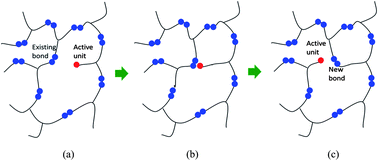
Covalent adaptable networks are polymers that can alter the arrangement of network connections by bond exchange reactions where an active unit attaches to an existing bond then kicks off its pre-existing peer to form a new bond. When the polymer is stretched, bond exchange reactions lead to stress relaxation and plastic deformation, or the so-called reforming. In addition, two pieces of polymers can be rejoined together without introducing additional monomers or chemicals on the interface, enabling welding and reprocessing. Although covalent adaptable networks have been researched extensively in the past, knowledge about the macromolecular level network alternations is limited. In this study, molecular dynamics simulations are used to investigate the macromolecular details of bond exchange reactions in a recently reported epoxy system. An algorithm for bond exchange reactions is first developed and applied to study a crosslinking network formed by epoxy resin DGEBA with the crosslinking agent tricarballylic acid. The trace of the active units is tracked to show the migration of these units within the network. Network properties, such as the distance between two neighboring crosslink sites, the chain angle, and the initial modulus, are examined after each iteration of the bond exchange reactions to provide detailed information about how material behaviors and macromolecular structure evolve. Stress relaxation simulations are also conducted. It is found that even though bond exchange reactions change the macroscopic shape of the network, microscopic network characteristic features, such as the distance between two neighboring crosslink sites and the chain angle, relax back to the unstretched isotropic state. Comparison with a recent scaling theory also shows good agreement.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...