Modulating the local structure of glass to promote in situ precipitation of perovskite CsPbBr3 quantum dots by introducing a network modifier†
Abstract
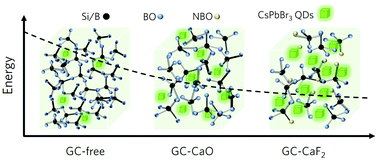
All-inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots (QDs) with high quantum efficiency (QE) and exceptional color purity show great potential in the field of wide-color-gamut backlit displays. However, their fragile stability is considered as a crucial obstacle towards their practical applications. Herein, high-quality CsPbBr3 QDs were regulated to be precipitated in borosilicate glass by introducing a network modifier, CaF2, which not only gives high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) and external quantum efficiency (EQE) up to 44.3% and 34.6% upon 455 nm excitation, respectively, but also presents a narrow bandwidth (FWHM of 26 nm). The roles of Ca ions and F ions on the nucleation/growth of CsPbBr3 QDs in glass (CsPbBr3 QDs@glass) are revealed in detail. Benefitting from superior optical performance and high stability of the CsPbBr3 QDs@glass composite, a white LEDs covering 127% of NTSC 1953 standard was fabricated and its potential application in LCD screens was also demonstrated. This study provides a guide for the synthesis of CsPbBr3 QDs embedded glasses with high QE by introducing the related nucleation inducing agents and increasing the interstitial space.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...