Nano-scale mechanics of colloidal C–S–H gels
Abstract
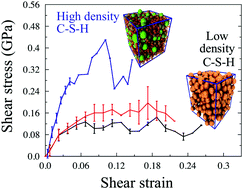
Gels of calcium–silicate–hydrates (C–S–H) are the glue that is largely responsible for the mechanical properties of cement. Despite their practical relevance, their nano-scale structure and mechanics are still mainly unexplored, because of the difficulties in characterizing them in a complex material like cement. We propose a colloidal model to investigate the gel mechanics emerging in the critical range of length-scales from several tens to hundreds of nanometers. We show that the size polydispersity of the hydrates and size-dependent effective interactions can explain the mechanical heterogeneities detected in nano-indentation experiments. We also show how these features control the arising of irreversible structural rearrangements under deformation, which are good candidates as nano-scale mechanisms underlying mechanical aging and slow structural relaxation in the gels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...