Hydrogen sulfide removal from natural gas using membrane technology: a review†
Abstract
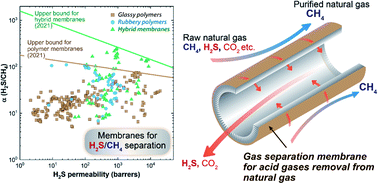
Natural gas, having a significantly lower CO2 emission factor than oil and coal when combusted, is accepted as an important transition fuel towards carbon net-zero society. To meet the calorific value requirements (≥34.0 MJ m−3) and reduce possible corrosion of transportation pipelines, acid gases such as CO2 and H2S must be removed from raw natural gas. Membrane separation is a promising alternative approach to remove acid gases from natural gas. This paper aims to review the development of various polymer-based membranes and membrane processes for H2S separation from natural gas. Progress in glassy polymer membranes, rubbery polymer membranes, hybrid membranes and membrane contactors for H2S removal from natural gas is summarized and analyzed. The H2S separation performance of various membranes is plotted in one diagram and a new H2S/CH4 upper bound is proposed. Challenges of membranes for H2S separation and prospects of future development are thoroughly discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...