AgPt/MoS2 hybrid as electrochemical sensor for detecting H2O2 release from living cells†
Abstract
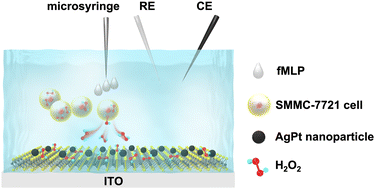
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), as a biomarker in a series of physiological processes, plays a crucial role in investigating the pathogenesis of some diseases. The highly sensitive and selective detection of H2O2 release from living cells has aroused tremendous research interests. Herein, a non-enzymatic electrochemical H2O2 biosensor was constructed based on AgPt bimetallic nanoparticle-structured MoS2 nanohybrid (AgPt/MoS2) as an electrocatalyst. The AgPt/MoS2 nanohybrid was successfully synthesized by a facile wet-chemical method. Compared with AgPt nanoparticles, the AgPt/MoS2 nanohybrid exhibited significant enhancement in catalytic performance towards H2O2. The main factor is that MoS2 nanosheets as a supporting material promote AgPt nanoparticles to expose more active sites. The electrochemical response of the AgPt/MoS2 hybrid-based biosensor to H2O2 was linear in the range of 20 μM–4 mM, and the detection limit was calculated as 1.0 μM. To prove practicality, the biosensor was further applied to detect H2O2 release from living SMMC-7721 cells. These results indicate the potential applications of the developed biosensor in monitoring physiological processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...