BINOL-based chiral aggregation-induced emission luminogens and their application in detecting copper(ii) ions in aqueous media†
Abstract
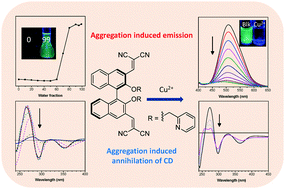
Two novel chiral luminogens BINOM-CN and BINOP-CN derived from (R)-1,1′-binaphthol (BINOL) with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics were designed and synthesized. Dicyanomethylene and the substituent of the hydroxyl group have been found to be the key structural element for this unique AIE effect. Meanwhile, these two chiral AIE luminogens exhibit abnormal aggregation-induced annihilation of the circular dichroism (CD) signal, which is ascribed to the decrease of the dihedral angle between adjacent naphthalene rings in the aggregation state. With the assistance of the pyridine unit, BINOP-CN can serve as an excellent sensor for Cu2+. In the presence of Cu2+, the fluorescence intensity and CD signals of BINOP-CN both decreased observably due to its ideal coordination with Cu2+, which was further confirmed by X-ray crystallography. Moreover, the addition of Cu2+ can induce the self-assembly of BINOP-CN.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...