Regulating TiO2/MXenes catalysts to promote photocatalytic performance of highly selective oxidation of d-xylose†
Abstract
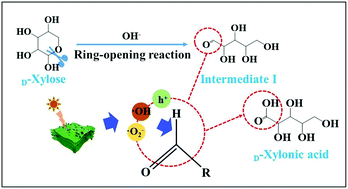
Synthesis of D-xylonic acid, a high value chemical feedstock, from biomass chemicals through a photocatalytic process is of great significance in respect of economical and sustainable concerns, and therefore has aroused considerable attention. Herein, a TiO2/Ti3C2(TT) photocatalyst was designed for the oxidation of xylose to D-xylonic acid under ambient conditions. The photocatalyst is fabricated by in situ growth of TiO2 nano-particles on Ti3C2 nanosheets and exhibits 64.2% of D-xylonic acid yield with excellent stability. The mechanistic study indicates that the electron transfer from TiO2 to Ti3C2 significantly increases the life time of light-induced charge carriers, and hence improved photocatalytic performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...