Effects of biological buffer solutions on the peroxidase-like catalytic activity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles†
Abstract
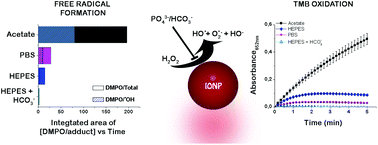
Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) are frequently used in biomedical applications due to their magnetic properties and putative chemical stability. Nevertheless, their well-known ability to mimic some features of the peroxidase enzyme activity under specific conditions of pH and temperature could lead to the formation of potentially harmful free radical species. In addition to the intrinsic enzyme-like activity of IONPs, the buffer solution is an important external factor that can alter dramatically the IONP activity because the buffer species can interact with the surface of the particles. In our study, IONP activity was evaluated in different buffering solutions under different experimental conditions and predominant free radical species were measured by electron paramagnetic resonance using the spin-trap 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO). The formation kinetics of the reactive oxygen species were studied by UV-visible spectroscopy with TMB and DAB peroxidase substrates. We found that the highest catalytic oxidation of peroxidase substrates and free radical generation were achieved in acetate buffer, while phosphate buffer inhibited the peroxidase-like activity of IONPs in a concentration dependent manner. When emulating the physiological conditions, a lower catalytic activity was observed at pH 7.4 when compared to that at pH 5.0. Also, in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), we observed an enhancement in the peroxidase substrate oxidation rate that was not accompanied by an increase in DMPO/adduct formation which could be related to a non-specific oxidation catalyzed by the chloride ion. Similar observations were found after the addition of a bicarbonate to HEPES buffer. TMB oxidation did not occur when the reaction was conducted with free iron ions from metal salts with the same concentration of the IONPs (0.33 Fe2+ and 0.66 Fe3+). However, we observed even higher catalytic activities than those when doubling the IONP concentration when they are combined with the free iron salts. These results indicate that biological buffering solutions need to be carefully considered when evaluating IONP catalytic activity and their potential toxicological effects since under physiological conditions of pH, salinity and buffering species, the peroxidase-like activity of IONPs is dramatically reduced.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...