Zn(O,S)-based electron-selective contacts with tunable band structure for silicon heterojunction solar cells†
Abstract
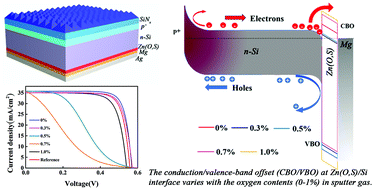
Recently, there have been rapid advances in silicon heterojunction (SHJ) solar cells based on dopant-free contacts. However, there is no better choice to achieve flexible energy band alignment than to choose different materials. Here, Zn(O,S) materials, whose energy band structure can be flexibly tuned by a continuously adjustable ratio of S/Zn, combined with a low work function Mg layer, contribute a novel electron-selective contact (ESC) for Si-based dopant-free heterojunction solar cells. The tunability of the energy band structure of the ESC is confirmed by ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, originating from the modulation of chemical composition by the change in oxygen partial pressure using reactive sputtering, which is linked to the Zn(O,S)/n-Si interface properties and the corresponding solar cell device performances. Zn(O,S) films with a high ratio of S/Zn present a small conduction band offset (CBO) and a large valence band offset (VBO) at the Zn(O,S)/n-Si interface, which reduces minority carrier recombination and favors majority carrier transport, and then contributes to an absolute efficiency gain of 1.9% compared with the reference cell. In contrast, the Zn(O,S) films with a low ratio of S/Zn present a large CBO at the Zn(O,S)/n-Si interface, which makes the solar cell J–V curve exhibit an anomalous S-shape with a degraded fill factor (FF). A similar J–V distortion trend is found in simulated results when the value of the CBO at the Si/Zn(O,S) interface goes from small to large. These results offer a concept of energy-band-tunable ESCs for constructing new dopant-free contacts to realize high-performance photovoltaic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...