Grape seed procyanidins suppress the apoptosis and senescence of chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritis via the DPP4-Sirt1 pathway
Abstract
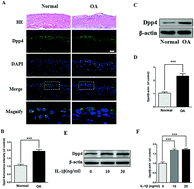
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a complicated pathological condition affecting thousands of people around world, many with substantial unmet medical care needs and without any effective therapies. Previous study has indicated that glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is involved in the pathological progress of osteoarthritis; however, the role of dipeptidase-4 (DPP4), which regulates the degradation of GLP-1, still remains unclear in osteoarthritis. Herein, after comparing normal mouse cartilage tissues with OA mouse cartilage tissues by histological analysis, we found out that DPP4 was highly expressed in OA cartilage tissues. To investigate the role of DPP4 in osteoarthritis, the apoptosis and senescence of chondrocytes were found to be decreased in vitro when DPP4 was downregulated by siRNA in chondrocytes. Further study showed that the inhibition of DPP4 by procyanidins, a grape seed extract, attenuated apoptosis and senescence of chondrocytes in vitro. Furthermore, the results showed that DPP4 inhibition protects cartilage by activating Sirt1, which has been reported to be associated with many pathophysiological processes, particularly in age-related diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders and osteoarthritis. In addition, animal experiment results demonstrated that procyanidins were capable of ameliorating the progression of osteoarthritis through the inhibition of DPP4. This study provides a competitive target for the therapeutic treatment of osteoarthritis, and procyanidins were shown to be a potential medicine for the restoration of the effects of osteoarthritis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...