IrO2-incorporated La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 as a bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst with enhanced activities†
Abstract
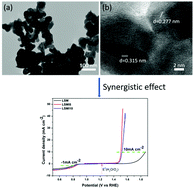
Developing low-cost and highly efficient oxygen electrocatalysts for both the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) has become one important issue recently due to the sluggish kinetics of these two reactions, which require high overpotentials and thus high energy input. Perovskite oxides have emerged as a new class of highly efficient non-precious metal catalysts for oxygen electrocatalysis in alkaline media. In this work, an IrO2-incorporated La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 composite has been developed as a novel bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst using a polymer-assisted approach with a subsequent wet impregnation–calcination method. Due to the synergistic effect between the high ORR activity of La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 and the good OER activity of IrO2 as well as the improved electrochemically active surface area, the electrocatalytic activities of the composite for both the OER and ORR have been improved, compared with those of the pristine La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 (ΔE = 1.043 V), resulting in its enhanced bifunctionality (ΔE = 0.652 V) as an oxygen catalyst in alkaline solution, which is also superior to the reported state-of-the-art electrocatalysts. The stability test shows that after 1000 cycles of cyclic voltammetry (CV), there is only 15 mV positive shift for achieving a current density of 10 mA cm−2 in the OER and 17 mV negative shift to reach a current density of −1 mA cm−2 in the ORR, which indicates the good stability of the electrocatalyst (5 wt% IrO2 incorporated La0.8Sr0.2MnO3) in alkaline solution. Our study not only reports a new composite material as a bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst, but also opens a new avenue to develop novel perovskite oxide-based electrocatalysts with enhanced bifunctional electrocatalytic activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
