Thermally rearranged polymer membranes for desalination†
Abstract
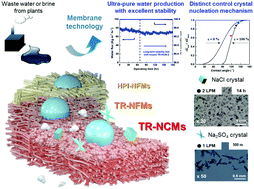
Herein, we demonstrate thermally rearranged polybenzoxazole-co-imide (TR-PBOI) electrospun nanocomposite membranes for membrane distillation and membrane crystallization applications. We seek to demonstrate that a synergistic combination of TR polymers, porous nanofibrous membranes, and particle coating improves the long-term stability while maintaining high porosity and water flux. The fabricated membranes exhibit an excellent water flux (80 kg m−2 h−1) and NaCl rejection (>99.99%) with steady performance over more than 186 hours. In addition, for the first time, controlling the heterogeneous nucleation phenomena in membrane crystallization was clearly demonstrated using TR membrane morphology.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...