Amorphous titanic acid electrode: its electrochemical storage of ammonium in a new water-in-salt electrolyte†
Abstract
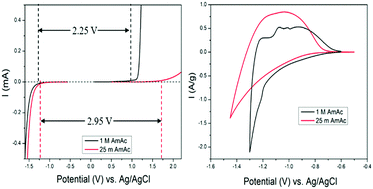
We report an amorphous titanic acid of TiO1.85(OH)0.30·0.28H2O as a new electrode for aqueous ammonium-ion batteries, which operates in a new water-in-salt electrolyte—25 m NH4CH3COO. The titanic acid electrode exhibits a specific capacity nearly 8 times that from the crystalline TiO2 electrode. In electrochemical reactions, the amorphous titanic acid provides abundant storage sites in its disordered structure and affords strong H-bonding toward the inserted NH4+ ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
