Electrochromic capacitive windows based on all conjugated polymers for a dual function smart window†
Abstract
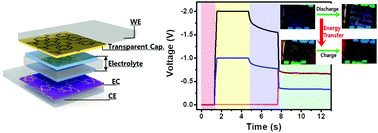
A highly transparent electrochromic capacitive (ECC) window was explored by combining a high contrast electrochromic polymer (ECP) and a transparent capacitive polymer. A blue and a red color ECP, poly(3,3-bis(bromomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-thieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxepine) (PR-Br) and poly(3,4-di(2-ethylhexyloxy)thiophene-co-3,4-di(methoxy)thiophene) (Th-OR), respectively, were introduced into an ECC window having a thin polyaniline (PANI) film as a capacitive layer. The as prepared ECC window showed high transparency (>72% for PR-Br), large color contrast, and long capacitive stability over 10 000 cycles, by combining non-aqueous acidic electrolyte and precise control of each electrode's working potential using in situ potential matching. Upon introducing a dielectric poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) layer, the blue ECC window made of PR-Br and PANI showed bistable ECC properties, along with a high energy density of 9.7 and 13.5 W h kg−1 with a power density of 75.3 and 58.8 kW kg−1, respectively, for bleaching and coloring. The red ECC window made of Th-OR and PANI also showed a high energy density (10.5 W h kg−1). The energy stored in an ECC window could be transferred to another device, like a battery, to switch the color or to light a LED when the ECC window is connected in series. Thus the ECC window in this study functions as a color switching smart window and a rechargeable battery, to provide a new path to achieve energy saving EC windows with multi-color tunability. The working principle of these ECC windows can be widely applied in various electrochemical devices for multiple functions in one device.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...