The reaction of activated esters with epoxides for self-curable, highly flexible, A2B2- and A3B3-type epoxy compounds†
Abstract
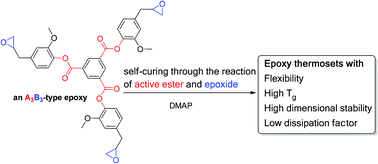
To achieve high-Tg and low-dissipation epoxy thermosets, bis(2-methoxy-4-(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)phenyl)isophthalate (2) and tris(2-methoxy-4-(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)phenyl)benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate (3) were prepared. DSC, IR, and solubility analyses have demonstrated that both (2) and (3) exhibit a self-curing characteristic in the presence of 0.5 wt% 4-dimethylaminopyridine. To understand the self-curing mechanism, a model compound, 2-methoxy-4-(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)phenyl acetate (1), was prepared. Through NMR analysis of (1) isothermal at 160 °C, a reaction of active ester (Ar–O–C(![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O)–) and epoxide moieties was observed. Therefore, if we consider an active ester group as A and an epoxide group as B, then (1), (2), and (3) are self-curable AB-type, A2B2-type, and A3B3-type epoxy compounds, respectively. Experimental data show that self-curing thermosets display a high Tg (207 °C), low thermal expansion (30 ppm °C−1), and low dissipation factor (0.0078). The findings provide a new design strategy for preparing high-Tg and low-dissipation epoxy thermosets.
O)–) and epoxide moieties was observed. Therefore, if we consider an active ester group as A and an epoxide group as B, then (1), (2), and (3) are self-curable AB-type, A2B2-type, and A3B3-type epoxy compounds, respectively. Experimental data show that self-curing thermosets display a high Tg (207 °C), low thermal expansion (30 ppm °C−1), and low dissipation factor (0.0078). The findings provide a new design strategy for preparing high-Tg and low-dissipation epoxy thermosets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...