Si nanoparticle clusters in hollow carbon capsules (SNC@C) as lithium battery anodes: toward high initial coulombic efficiency†
Abstract
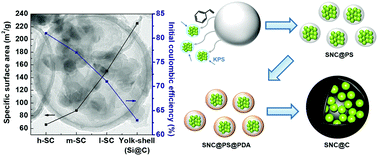
Large volumetric expansion and structural pulverization have been major problems in Si-based anode materials for Li-ion batteries. To overcome this limitation, yolk–shell structured Si–carbon structures have been proposed to allow for the reversible structural breathing of Si nanoparticles confined inside the carbon shell. However, initial coulombic efficiency (ICE) of the yolk–shell structured anodes is highly decreased mainly due to their extremely high specific surface area (SSA) and the resulting excessive formation of solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) over the carbon shell. Here, instead of using a single Si nanoparticle-containing yolk–shell structure, we propose a novel structure comprising hollow carbon capsules internally encapsulating Si nanoparticle clusters (SNC@Cs). To implement this structural design, Si nanoparticle clusters are encompassed by a polystyrene matrix (SNC@PS) by emulsion polymerization, followed by coating with a polydopamine (PDA) layer (SNC@PS@PDA). Then, after annealing them for carbonization, SNC@Cs are finally prepared, which can decrease the SSA by a factor of one-third compared to the conventional yolk–shell structures. These SNC@C particles have shown remarkably high ICE values of up to 81%. Moreover, the cycling stability could be improved up to 100 cycles because the properly confined Si cluster inside the stable carbon capsule mitigates structural pulverization during repeated lithiation–delithiation processes of Si nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...