Stable lithium metal anodes enabled by inorganic/organic double-layered alloy and polymer coating†
Abstract
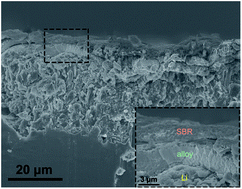
Lithium metals have been considered as the most promising anode materials for next-generation rechargeable batteries due to their high theoretical capacity and low potential. Unfortunately, lithium metal anodes (LMAs) usually suffer from immoderate dendrite growth during the cycling process, which can cause serious safety concerns. Herein, we develop an alloy/polymer double-layered protective coating as an artificial solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) to mitigate the above problem. The inorganic alloy (LiF-rich Li–Sb) layer is lithiophilic with high Li-ion conductivity, enabling dendrite-free plating/stripping of lithium at a high capacity. The organic polymer (commercial rubber) layer is highly flexible, keeping the artificial SEI stable during cycling. The use of double-layered coating results in significantly improved cycling stability for LMAs (500 h for a symmetric cell with a capacity of 1 mA h cm−2) in both ether- and carbonate-based electrolytes, which is much better than for cells employing pristine lithium or single-alloy-protected lithium. It should be noted that the Li–Sb alloy layer was created from a low-cost precursor (SbF3). We believe that the design of double layer protective coating using low-cost raw materials provides a new pathway to achieve dendrite-free LMAs with an enhanced cycling life.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...