Nuclear quantum effects in enzymatic reactions: simulation of the kinetic isotope effect of phenylethylamine oxidation catalyzed by monoamine oxidase A
Abstract
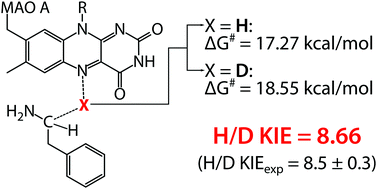
The kinetic isotope effect (KIE) is arguably the most established experimental observable reflecting nuclear quantum effects in enzymatic reactions. The role of nuclear quantum effects in enzymes is rather intriguing and has long been a source of profound investigations. Herein, we present a computational study of monoamine oxidase A (MAO A) enzyme and its substrate phenylethylamine, focusing on the impact of nuclear quantum effects on the reaction free energy barrier. Two distinct schemes of quantization of nuclear motion were used, one being the established Quantum Classical Path (QCP) approach, and the other our own code for quantum treatment along the selected nuclear coordinate (hydrogen transfer coordinate) which reasonably mimics the reaction coordinate. In excellent agreement with the experimental value of 8.5 ± 0.3, H/D KIE was computed to 8.66, corresponding to the D–H barrier difference of 1.28 kcal mol−1. The magnitude of KIE implies that nuclear quantum effects probably have only a minor role in the reaction, which is in accordance with the features of potentials computed along the reaction coordinate and with the pertinent energy levels and wavefunctions. The computed H/D KIE for the same reaction in aqueous solution and in the gas phase was fairly similar to the one in the enzyme, suggesting that the role of tunneling in the catalytic function of MAO A is insignificant. The agreement between the computed and observed KIE supported by analysis of nuclear quantum effects implicitly validates the assumed hydride transfer reaction mechanism.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...